Quick sort is a very efficient sorting algorithm invented by C.A.R. Hoare.
It has two phases:
- the partition phase and
- the sort phase
Quick sort is the fastest internal sorting algorithm with the time complexity O (n log n). The basic algorithm to sort an array a[ ] of n elements can be described recursively as follows:
Algorithm for Quick Sort
1. If n < = 1, then return.
2. Pick any element V in a[]. This is called the pivot.
3. Rearrange elements of the array by moving all elements xi > V right of V and all elements xi < = V left of V. If the place of the V after re-arrangement is j, all elements with value less than V, appear in a[0], a[1] . . . . a[j - 1] and all those with value greater than V appear in a[j + 1] . . . . a[n - 1].
4. Apply quick sort recursively to a[0] . . . . a[j - 1] and to a[j + 1] . . . . a[n - 1].

Visualization of the quicksort algorithm. The horizontal lines are pivot values.
Source Code
void quick_sort(int[],int,int);
int partition(int[],int,int);
void main()
{
int a[50],n,i;
printf("How many elements?");
scanf("%d",&n);
printf("\nEnter array elements:");
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
quick_sort(a,0,n-1);
printf("\nArray after sorting:");
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
printf("%d ",a[i]);
}
void quick_sort(int a[],int l,int u)
{
int j;
if(l<u)
{
j=partition(a,l,u);
quick_sort(a,l,j-1);
quick_sort(a,j+1,u);
}
}
int partition(int a[],int l,int u)
{
int v,i,j,temp;
v=a[l];
i=l;
j=u+1;
do
{
do
i++;
while(a[i]<v&&i<=u);
do
j--;
while(v<a[j]);
if(i<j)
{
temp=a[i];
a[i]=a[j];
a[j]=temp;
}
}while(i<j);
a[l]=a[j];
a[j]=v;
return(j);
}
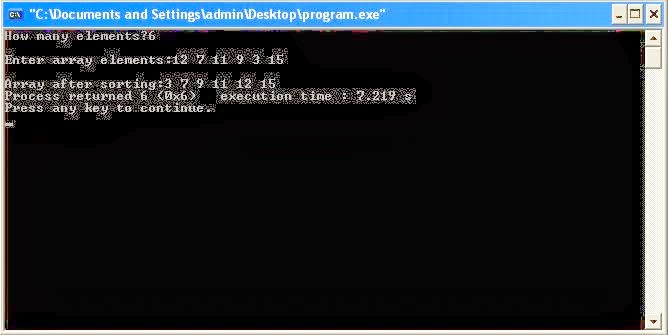
Output

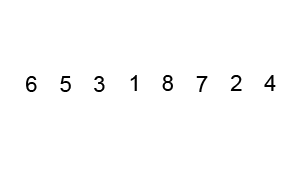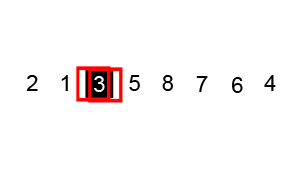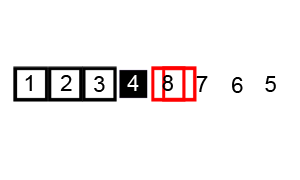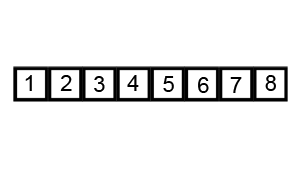







0 comments:
Post a Comment