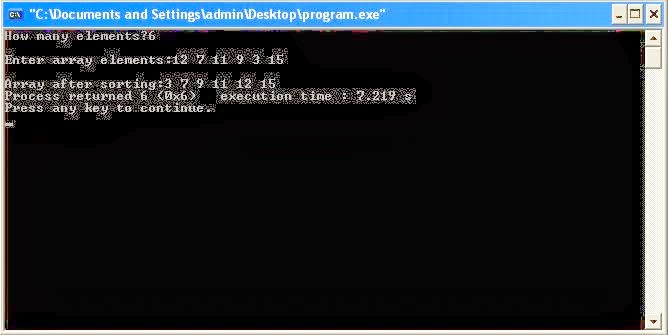
Hola Coders,
It’s been a long time since Fuzzyprograms launched, but now I am going to create summary type posts, So that You’ll get more info in single post than ever !
I am sharing 5 Graphical programs here. I know that using Graphics.h seems like a crime in 2013 but, Schools and Colleges are still teaching this. ( Obviously, Learning anything never goes in vain )
My belief is that, this will be very useful to students.
This program is submitted by : Ankit Kumar( ankit26kumar@gmail.com )It’s been a long time since Fuzzyprograms launched, but now I am going to create summary type posts, So that You’ll get more info in single post than ever !
I am sharing 5 Graphical programs here. I know that using Graphics.h seems like a crime in 2013 but, Schools and Colleges are still teaching this. ( Obviously, Learning anything never goes in vain )
My belief is that, this will be very useful to students.
1. Google Page Design
Isn’t it amazing ?
Source Code
#include<iostream.h> #include<conio.h> #include<graphic.h> #include<math.h> void main() {clrscr(); int g=0,d; initgraph(&g,&d,"c:\turboc3\bgi"); setbkcolor(15); setcolor(1); settextstyle(3,0,5); outtextxy(190,140,"G"); setcolor(4); settextstyle(3,0,5); outtextxy(220,140,"O"); setcolor(3); settextstyle(3,0,5); outtextxy(250,140,"O"); setcolor(1); settextstyle(3,0,5); outtextxy(280,140,"G"); setcolor(2); settextstyle(3,0,5); outtextxy(310,140,"L"); setcolor(4); settextstyle(3,0,5); outtextxy(340,140,"E"); setcolor(1); settextstyle(3,0,5); setcolor(4); settextstyle(1,0,2); outtextxy(100,350,"SEARCH"); settextstyle(1,0,2); outtextxy(380,350,"I'M FEELING LUCKY"); setcolor(8); rectangle(140,200,480,230); rectangle(93,350,183,380); rectangle(370,350,580,380); getch(); }
2. Taj Mahal Drawing
A Great Monument from India (Feeling proud). Excellent Program !
Download Source Code: Click Here
3. 3D Car Handling
I have no words for this one, Amazing Effects and Animation !
I recommend you all that you must Compile and Execute this one.
Download Source Code: Click Here
4. Flowerpot Design
I am not saying anything, Just Execute it and see the output.
Download Source Code: Click Here
5. Classic Car Game
Well, Yeah ! Everybody has played this game before, at least those who were born in 90′s. :DIt’s time to play again, then. (But also understand the code)
Info by Coder : This is a car race game, and i generated random cars in front of your car. you have to dodge all the cars. The control is highly sensitive, You have to make the move on time. I have used graphics to develop this game.



.png)